How to run Z-Image Turbo on Google Colab for Text-to-Image

How to Run Z-Image Turbo on Google Colab
In this guide, I show how to run Z-Image Turbo, a text-to-image model, on Google Colab. I cover setup, model installation, a simple generation function, prompt usage, runtime limits, and practical tips for managing memory and reconnections on the free Colab tier.
Model versions and what we will use
The model comes in three versions:
- Z-Image Turbo
- Z-Image Base
- Z-Image Edit
For this walkthrough, I use Z-Image Turbo.
Quick online try on Hugging Face
You can try the model here by entering a prompt and clicking Generate. The checkpoint is available there, and the Colab setup below downloads what is needed from that source.
Set up the Google Colab runtime First
I provide a Colab notebook link for this setup. Open it to get started.
Connect to a T4 GPU
- Click Connect.
- Select a T4 GPU.
- Wait for the runtime to attach.
- Once connected, proceed to installation.
Install and prepare the environment
- Click Install and then Run anyway if prompted.
- The notebook installs required packages and dependencies.
Why ComfyUI instead of Diffusers
I do not use Diffusers in this setup. I use ComfyUI. The process is:
- Install ComfyUI requirements.
- Download the necessary models.
- Load ComfyUI code.
- Define a generate function to run image creation.
What the notebook installs and downloads
The install cell:
- Installs ComfyUI requirement packages.
- Downloads the Z-Image Turbo model checkpoint from Hugging Face.
- Sets up the ComfyUI nodes used by the generation function.
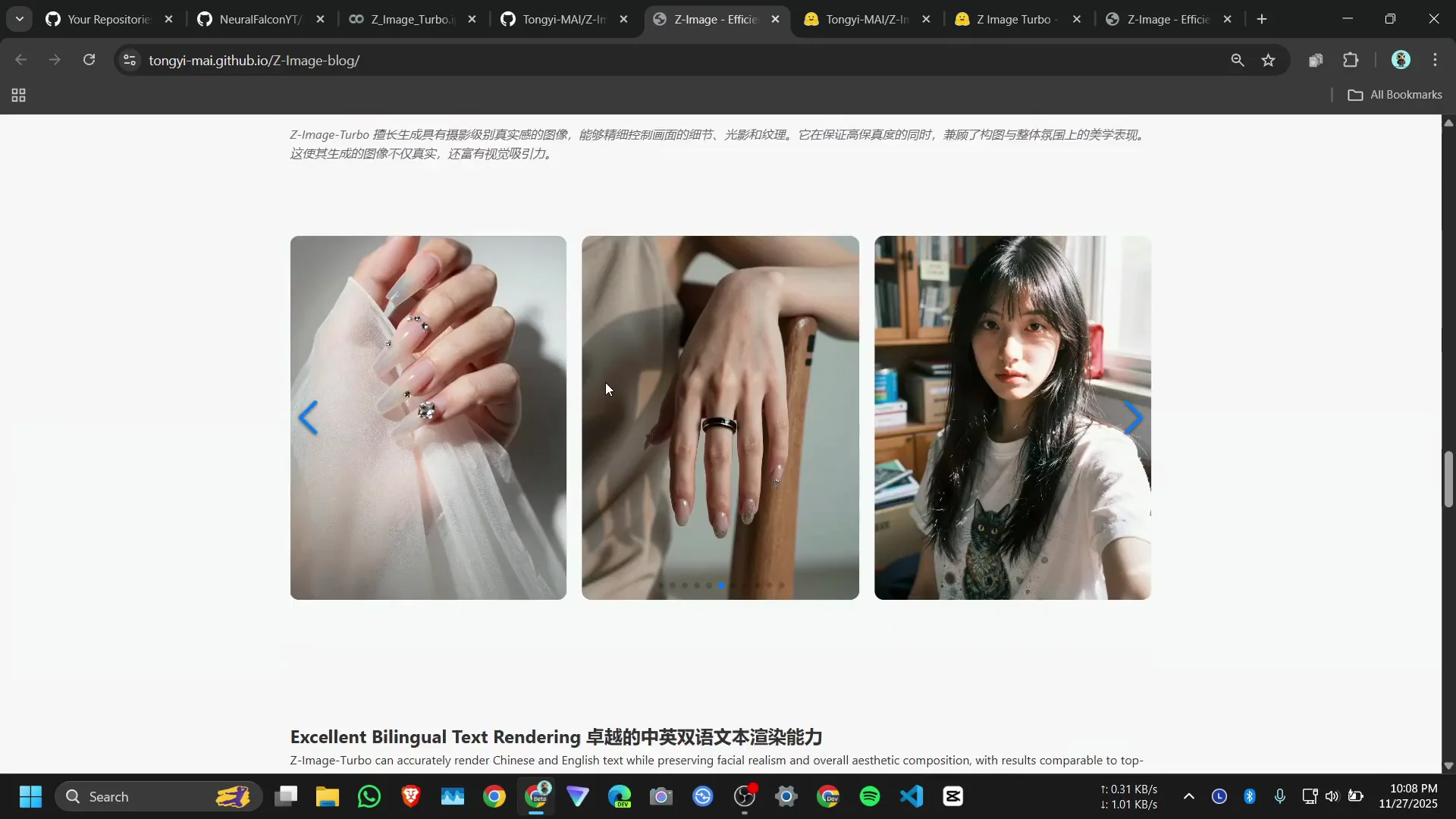
While installation completes, note that the official demo shows clear image quality. The model can respond to location references, such as generating landmarks accurately when prompted.
Build the generation function
Once packages and models are installed, the notebook defines helper code and a simple generation function.
Utility imports from ComfyUI
A utility cell imports nodes from ComfyUI. This provides the building blocks used by the generation function.
Function inputs and parameters
The generation function accepts:
- Positive prompt
- Negative prompt
- Aspect ratio
- Seed
- Steps
- CFG
- Denoise
What the model outputs depends on your prompt and these parameters.
Parameter reference
| Parameter | What it controls | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Positive prompt | What you want the image to contain | Core driver of results |
| Negative prompt | What you want to avoid | Helps reduce unwanted artifacts |
| Aspect ratio | Output dimensions ratio | Example ratios include 1:1 and 9:16 |
| Seed | Randomness source | Set to 0 for a random seed |
| Steps | Number of sampling steps | Higher steps can increase detail but use more time |
| CFG | Classifier-free guidance | Higher values push outputs closer to the prompt |
| Denoise | Strength of denoising | Adjusts how strongly noise is removed |
Prompt sourcing and first run
I use a gallery site for a positive prompt and get a matching negative prompt from a text assistant.
Getting a positive prompt from an art gallery
I browse a public art gallery and copy a text-to-image prompt that fits what I want. The gallery has many prompts to choose from.
Getting a negative prompt
I generate a negative prompt with a text assistant to remove elements I do not want in the image. I paste this into the negative prompt field.
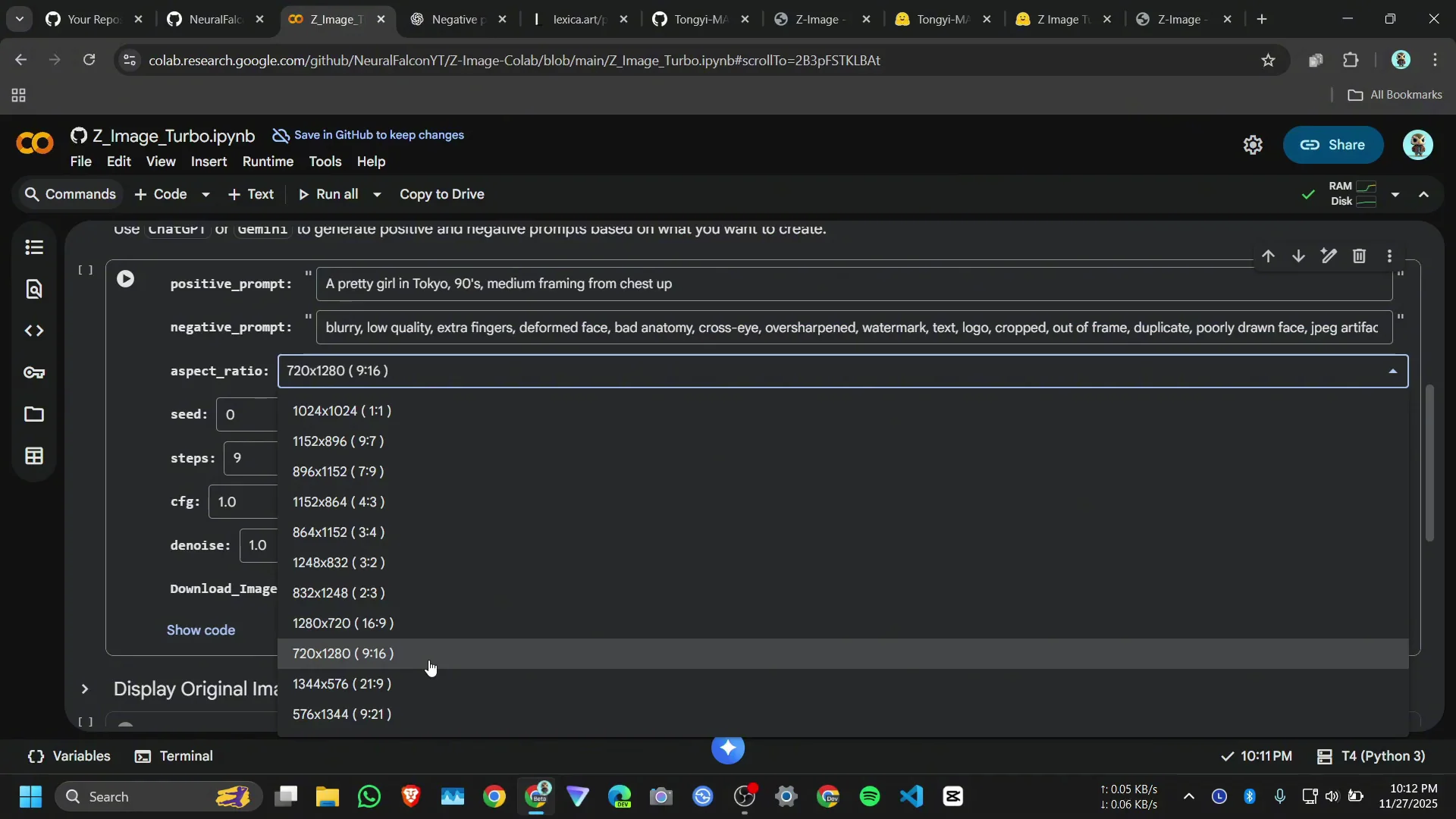
Aspect ratio and run
- I paste the positive prompt.
- I paste the negative prompt.
- I select a 9:16 aspect ratio.
- I click Run.
If you set the seed to 0, the notebook uses a random seed. For most users, positive prompt, negative prompt, and aspect ratio are enough to start.
Simple settings for most users
Recommended parameters to touch
- Positive prompt
- Negative prompt
- Aspect ratio
- Optionally, set Seed to 0 for randomness
You can adjust steps, CFG, and denoise later if you want to experiment.
Generation time per image
Each image takes about 2 to 2.5 minutes to generate on a T4 GPU in this setup.
Interface, memory limits, and disconnections
I added a small Gradio interface to reduce memory crashes on the free Colab tier.
Gradio interface to reduce crashes
The interface helps keep memory use manageable and limits the resolution to reduce RAM spikes that cause Colab to crash.
Resolution limits on free Colab
- Higher resolutions are more likely to exhaust memory.
- If you try 1080 by 1920, the session can crash.
- For stability, stay with the lower resolution provided in the notebook.
If the runtime disconnects
If Colab disconnects while generating:
- Run the QS code cell again.
- Run the next cell that sets up the generation function.
- Resume image generation.
Memory behavior during and after runs
- After an image is generated, GPU memory drops to about 9.9 GB.
- On reruns, CPU RAM settles around 5 GB.
This setup works on Colab, and fluctuations during generation are expected.
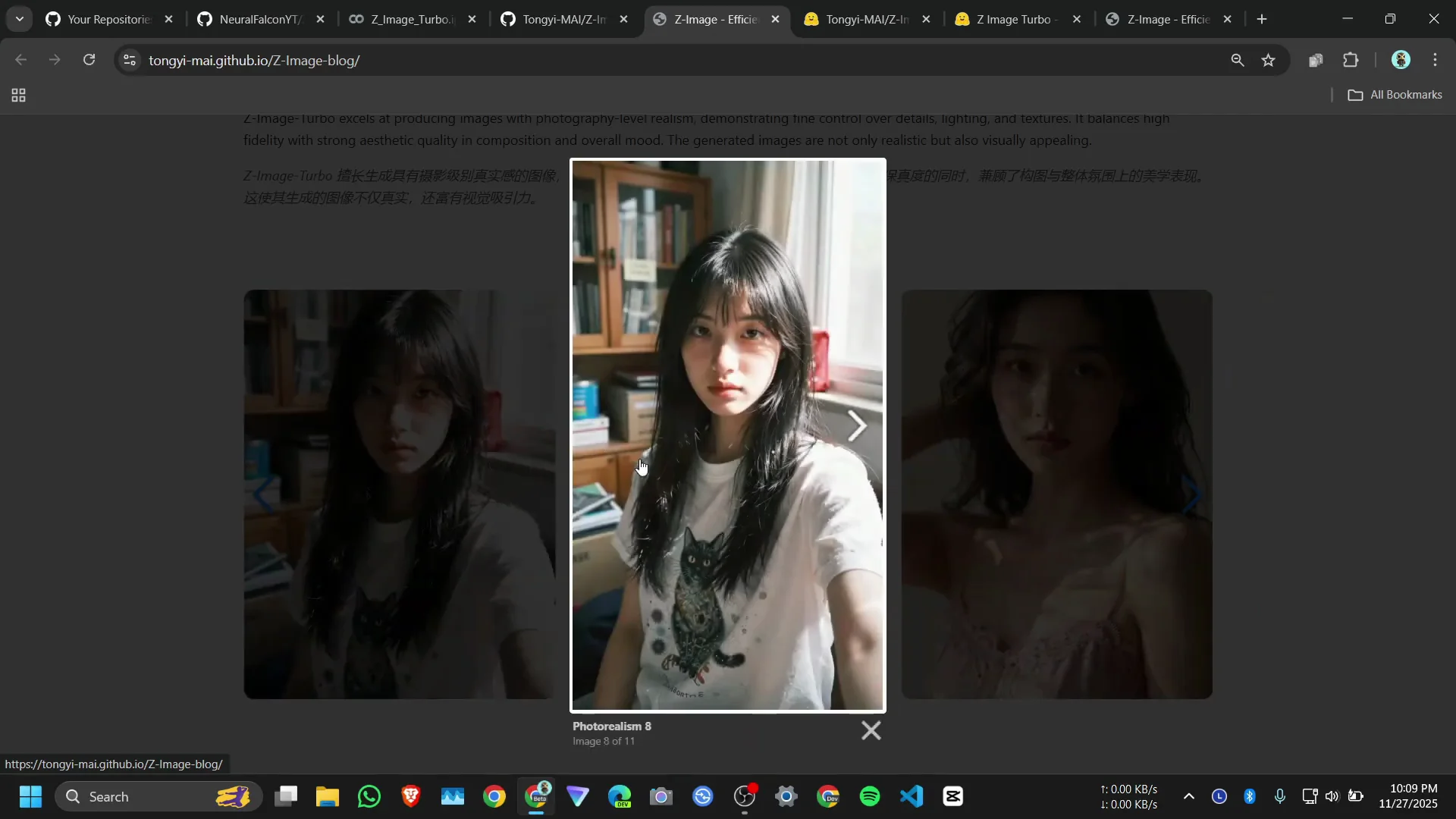
Preview, open, and download results
The notebook shows a small preview on the output cell. To view the original full-resolution preview, run the relevant preview cell. You can open the image in a new tab and click to download.
Additional runs and observations
I walk through a few different prompts and settings to show how the model behaves, including memory changes and visual quality.
Movie poster attempt
I paste a new positive prompt and a matching negative prompt for a poster-style image and run generation.
- System RAM goes down to about 5 GB to 4.5 GB during the process.
- The output may include blurred or random text elements. This is a known behavior and is not tied to specific names provided in the prompt.
Text artifacts and model size
Text rendering and naming can be unreliable. The model has about 6 billion parameters, and text elements can show blur or random words in outputs. Keep expectations modest for complex text layout.
Second run with different aspect and steps
I run another prompt with a square 1:1 aspect ratio. I then repeat with a 9:16 ratio and set steps to 10.
- The 1:1 output is acceptable.
- The 9:16 output looks better for that prompt.
- With 10 steps, the details are solid for the time spent.
Open the image in full screen from the output to view details. The original reference and the new result are visible in the notebook. The model runs fully on Google Colab within the free tier constraints.
Step-by-step: Run Z-Image Turbo on Google Colab
Use these steps in order and do not skip cells.
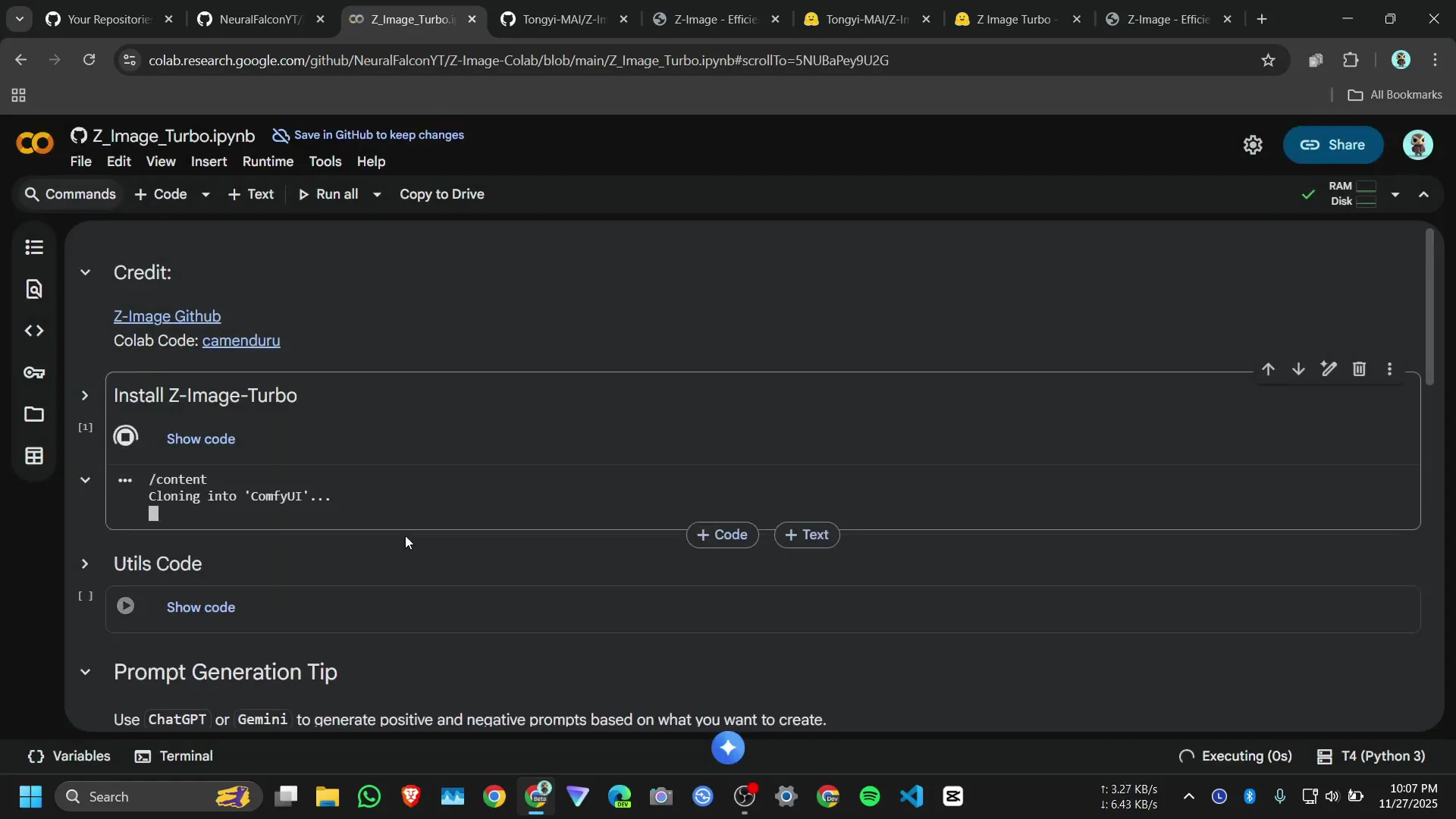
- Open the Colab link
- Use the provided notebook link.
- Allow the notebook to load.
- Connect to a GPU
- Click Connect.
- Select T4 GPU.
- Wait for the runtime to attach.
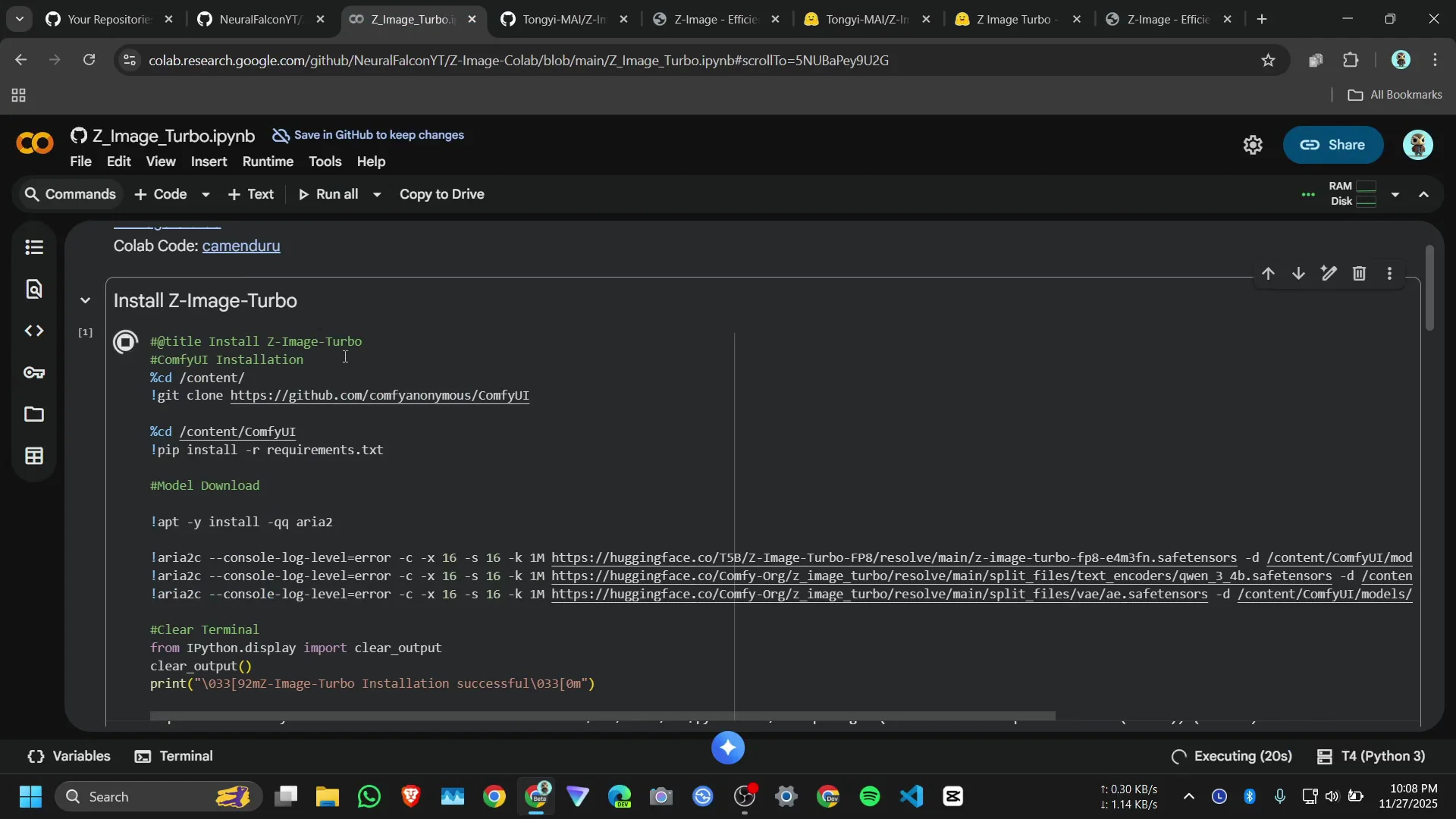
- Install dependencies
- Click the Install cell.
- Click Run anyway if prompted.
- Wait for ComfyUI requirements to complete.
- Download model files
- Run the cell that downloads the model checkpoint from Hugging Face.
- Wait for the checkpoint to finish downloading.
- Load ComfyUI nodes
- Run the utility cell that imports nodes from ComfyUI.
- Confirm there are no import errors.
- Define the generation function
- Run the cell that defines the generate function.
- The function accepts positive prompt, negative prompt, aspect ratio, seed, steps, CFG, and denoise.

- Prepare prompts
- Copy a positive prompt from a prompt gallery.
- Obtain a negative prompt from a text assistant.
- Paste both into the respective fields.

- Set parameters
- Choose an aspect ratio, such as 9:16 or 1:1.
- Set seed to 0 for random seed, or set a specific seed for reproducibility.
- Leave steps, CFG, and denoise at defaults if you are new.

-
Generate
- Click Run.
- Wait about 2 to 2.5 minutes per image.
-
Preview and download
- View the small preview.
- Run the original preview cell to see the full version.
- Open the image in a new tab.
- Click to download the image.
-
Handle disconnections
- If Colab disconnects, re-run the QS code cell.
- Re-run the generation function cell.
- Resume generation.
-
Manage memory
- Keep resolutions within the notebook default for stability.
- Expect GPU memory to drop to about 9.9 GB after a run.
- Expect CPU RAM to reduce to around 5 GB on subsequent runs.
Tips for prompts and settings
These pointers reflect how I worked with the notebook.
-
Start simple
- Use clear positive prompts and a concise negative prompt.
- Change only aspect ratio at first.
-
Adjust carefully
- If results are too loose, raise CFG slightly.
- If results are noisy, increase steps a bit.
- Keep an eye on runtime and memory impact when increasing steps.
-
Control randomness
- Set seed to 0 for a new random seed each time.
- Set a specific seed for consistency.
-
Mind text in images
- Expect blurred or random text elements.
- Do not rely on the model for precise text layout.
Troubleshooting on Colab
-
Session disconnects during generation
- Re-run the QS code cell.
- Re-run the generation function cell.
- Try generating again.
-
Memory errors at higher resolution
- Return to the default resolution in the interface.
- Keep aspect ratio changes within the provided presets.
- Avoid pushing to 1080 by 1920 on the free tier.
-
Slow or stuck cell
- Wait a few minutes, since each image can take 2 to 2.5 minutes.
- If it stalls for much longer, interrupt and re-run the last two cells.
What to expect from Z-Image Turbo on Colab
-
Image quality
- Clear images with good detail at the provided resolution.
- Location prompts are handled well.
-
Speed
- Around 2 to 2.5 minutes per image on a T4 GPU using this setup.
-
Stability
- Stable at default resolution.
- Crashes are more likely at higher resolutions.
-
Controls that matter most
- Prompts and aspect ratio shape the output the most.
- Steps, CFG, and denoise fine tune the result.
Run Z-Image Turbo on Google Colab: quick reference
- Use the provided Colab link.
- Connect to a T4 GPU.
- Install ComfyUI requirements.
- Download the model from Hugging Face.
- Import ComfyUI nodes with the util cell.
- Define the generate function.
- Paste positive and negative prompts.
- Choose aspect ratio and optional seed.
- Run and wait 2 to 2.5 minutes per image.
- Use the preview cells to view and download.
- If disconnected, re-run the QS code cell and the function cell.
- Keep resolution modest to avoid RAM crashes.
Closing notes
This workflow runs Z-Image Turbo fully in Google Colab using ComfyUI. It provides clean results at stable settings, with straightforward controls over prompts, aspect ratio, steps, CFG, and denoise. The notebook link is provided so you can reproduce the setup and try your own prompts. I will add the images I generated in the notebook for reference.
Recent Posts

How to Improve Text on Z-Image Turbo?
Z-Image-De-Turbo: A de-distilled variant of Z-Image-Turbo for flexible training, LoRA development, and extended experimentation without adapters.

Z-Image-De-Turbo de-distilled variant of Z-Image
Z-Image-De-Turbo: A de-distilled variant of Z-Image-Turbo for flexible training, LoRA development, and extended experimentation without adapters.
Z-Image Turbo ControlNet Workflow
Tutorial on Union ControlNet in ComfyUI—pose, Canny, and depth controls, depth-model preprocessing, step-by-step workflow, plus speed tests with example results.
Comments
Loading comments...